Role and structure of the Supreme Court
In this section:
- Role of the Supreme Court
- Organisational structure of the Supreme Court
Organisational structure of the Supreme Court

The Supreme Court is headed by the Chief Justice, who is supported by the:
The Supreme Court also includes the Singapore Judicial College, which serves the learning and development needs of judges and judicial officers.
The Supreme Court Bench
The Supreme Court Bench consists of the Chief Justice, Justices of the Court of Appeal, Judges of the Appellate Division, Judges of the High Court, Senior Judges, International Judges and Judicial Commissioners.
The Judges and Judicial Commissioners are appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. Judicial Commissioners are appointed to facilitate the disposal of business in the Supreme Court. They have the powers of a judge and are appointed for a specific period determined by the President.
A person may be appointed a Judge or Judicial Commissioner of the Supreme Court if they are a "qualified person" based on the definition in Section 2 of the Legal Profession Act, or have been a member of the Singapore Legal Service for at least 10 years, or both.
View the list of judges on the Supreme Court bench.
View the list of international judges who hear cases in the SICC.
View the Judicial Code of Conduct
(PDF, 262 KB) for the Judges and Judicial Commissioners of the Supreme Court.
The Supreme Court Registry
The Supreme Court Registry comprises the Division for the Court of Appeal and the Appellate Division, the Division for the General Division of the High Court, and the Division for the Singapore International Commercial Court (SICC).
The Registry is headed by the Registrar of the Supreme Court. The Registrar oversees the Registry’s management of the cases in the Supreme Court and is concurrently the Sheriff of the Supreme Court with responsibility over the execution of various writs and processes issued by the Supreme Court.
The Registrar is assisted by the Deputy Registrar, Senior Assistant Registrars, Divisional Registrars, Deputy Divisional Registrars and Assistant Registrars (collectively, “registrars”). Registrars are appointed by the President, on the recommendation of the Chief Justice. They hold concurrent appointments as District Judges or Magistrates.
Registrars are empowered to exercise the authority and jurisdiction of a Judge sitting in chambers in the General Division of the High Court (except such authority and jurisdiction specifically required to be exercised by a Judge in person). They perform judicial roles in hearing, deciding and issuing judgments on a wide range of civil matters, including interlocutory applications (e.g., summary judgment, striking out, further and better particulars, discovery, interrogatories), bankruptcy applications, examination of judgment debtor, taxation, enforcement matters (e.g., issue of warrant of arrest and release of vessel, issue of writs of seizure and sale) and ex parte matters. Registrars also conduct and preside over trials on assessment of damages and taking of accounts.
Registrars also deal with certain criminal matters, such as Criminal Case Disclosure Conferences. Registrars who are concurrently District Judges or Magistrates, may in those capacities, conduct committal hearings under Division 2 of Part X of the Criminal Procedure Code as in force immediately before 17 September 2018.
Working in close partnership with the Supreme Court Bench, registrars ensure the smooth and expeditious resolution of Supreme Court cases and matters docketed to specialised lists through active case management. To this end, registrars conduct Pre-Trial Conferences and Case Management Conferences for all Supreme Court matters, and also develop systemic enhancements in court procedures and processes through establishing best practices, bespoke guidelines and customised workflows.
Registrars support the Chief Justice and the Supreme Court Bench in advancing key strategic initiatives and judicial reforms to enhance the administration of justice. They are involved in innovative legislative reforms and reviews customised to the rules, procedures and requirements for matters at all levels in the Supreme Court. In view of their expertise and experience, registrars participate in and speak at international and local fora on the Singapore judicial system and issues relating to judicial policy and reform and specialised legal areas. They also contribute to the development of the law through editorship or authorship of academic publications and commentaries.
In addition, the Registry also manages issues relating to the profession (e.g., the admission of Advocates and Solicitors, functions of the Disciplinary Tribunal Secretariat and the registration of foreign lawyers in the SICC), as well as superintending and advising on the work of the various sections in the Legal Directorate of the Supreme Court.
View the list of registrars in the Supreme Court Registry .
Judiciary Administration
The Chief Executive (Office of the Chief Justice) oversees the integrated administration of the judiciary, ensuring the efficient running of the courts and provision of effective services to court users.
The integrated corporate functions of the three courts are:
| Access to Justice (A2J) Programme Office | Drives the judiciary’s transformation into a more outward-facing, user-centric organisation, through A2J advocacy, policy, planning, projects in partnership with stakeholders, and scaling up of best practices across all courts. |
| Communications and Service Excellence | Oversees the planning and execution of public engagement and communication efforts to position the SG Courts as a forward thinking, innovative and trusted judiciary. Facilitates equal and continuous access to justice through effective public service delivery. |
| Corporate Services | Oversees the SG Courts’ human resources, security, record management (for non-court records) and administrative functions as well as the respective libraries at the Supreme Court and State Courts. |
| Finance and Procurement | Promotes proper stewardship of the SG Courts’ financial resources, through the implementation of frameworks that promote financial prudence, value-for-money practices and financial accountability. |
| Infrastructure and Court Resources | Strategises and optimises the use of space, technology and resources that best support court hearings and operations to create excellent court experience for all court users. The Division comprises the Building Infrastructure Department, Court Infrastructure Department and Language Resources Department. |
| Innovation, Technology and Transformation | Coordinates and drives transformation to achieve consistency and to develop new approaches for the work of the judiciary; oversees the acquisition and deployment of technology in the judiciary. |
| Internal Audit | Adopts a risk-based approach to evaluate the adequacy of internal control systems, to enhance and protect organisational values, provide objective assurance, advice and insight, whilst ensuing compliance with government regulations, procedures and sound governance practices. |
| International Relations | Supports SG Courts’ international engagements on the bilateral, regional and multilateral fronts. Promotes effective and coherent responses to global threats through collaboration between judiciaries, dialogues, and sharing of best practices. |
| Knowledge Management Office | Advocates knowledge as a strategic asset for the entire judiciary through the establishment and implementation of common standards and policies in knowledge management to facilitate the sharing of knowledge and best practices across the courts. |
| Judicial Policy | Advances the SG Court’s position as a thought leader in court excellence through policy formulation, strategic planning, and international engagement. |
Judges and judicial officers in the Supreme Court
The Supreme Court Bench
There are currently 34 Judges (including the Chief Justice, 3 Justices of the Court of Appeal and 4 Judges of the Appellate Division, 4 Judicial Commissioners and 5 Senior Judges and 17 Judges of the High Court) and 24 International Judges on the Supreme Court Bench.
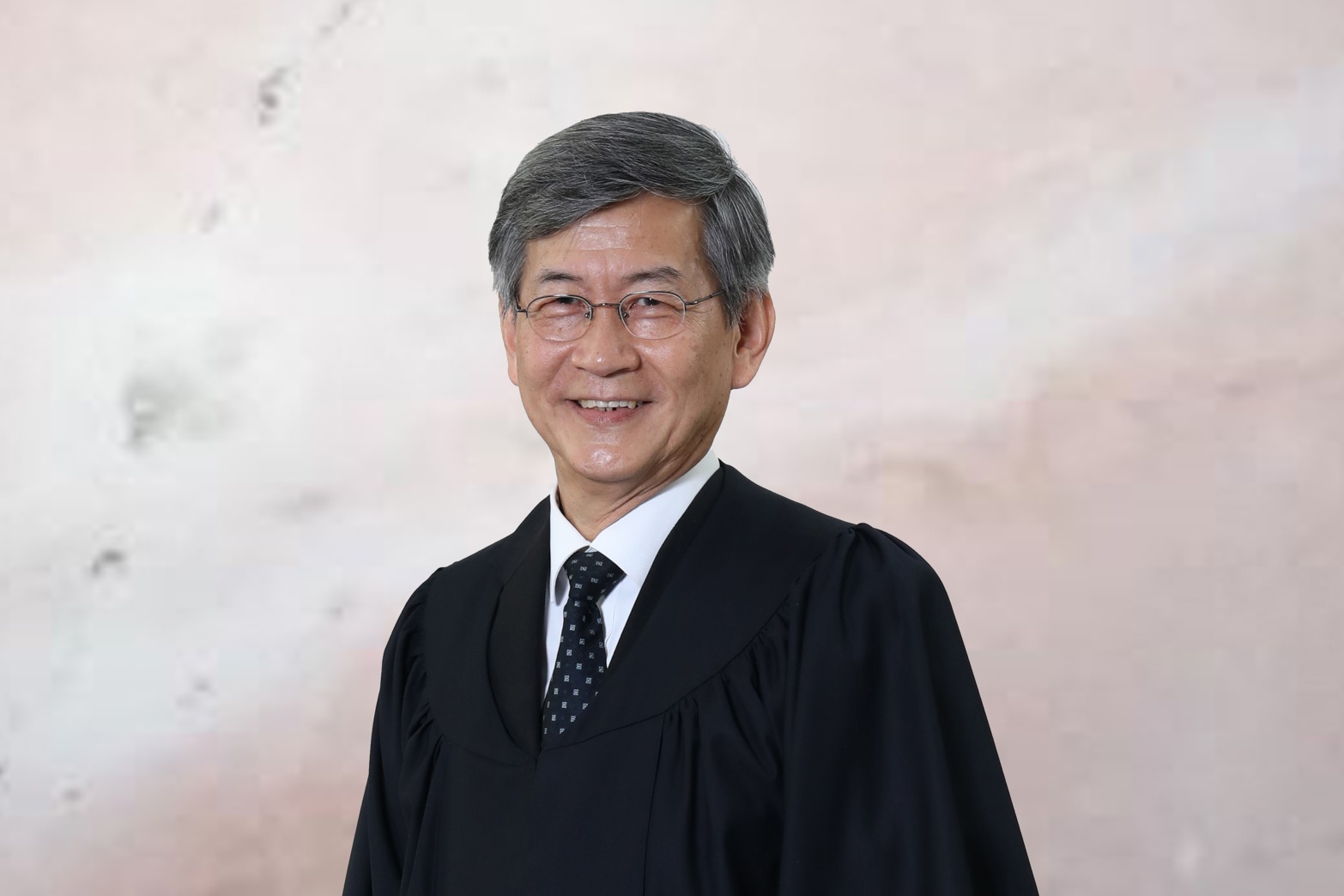
Chief Justice

Justices of the Court of Appeal
Judges of the Appellate Division
Justices
The Supreme Court Registry
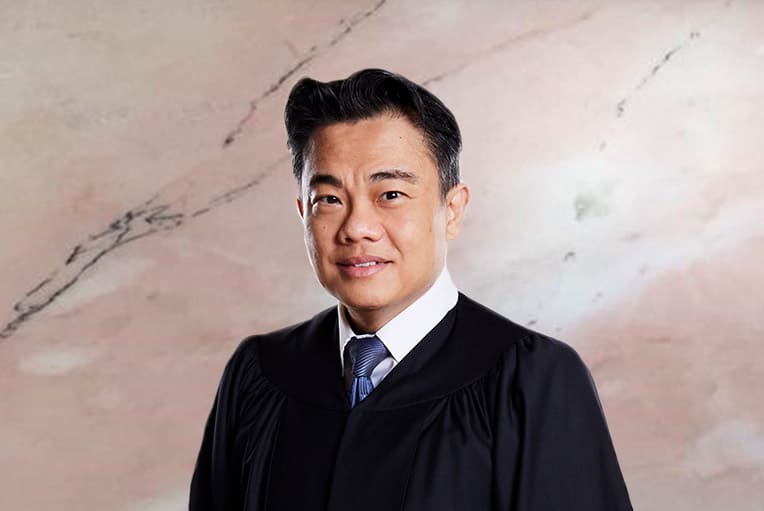
Registrar
Ms Jill Tan Li Ching
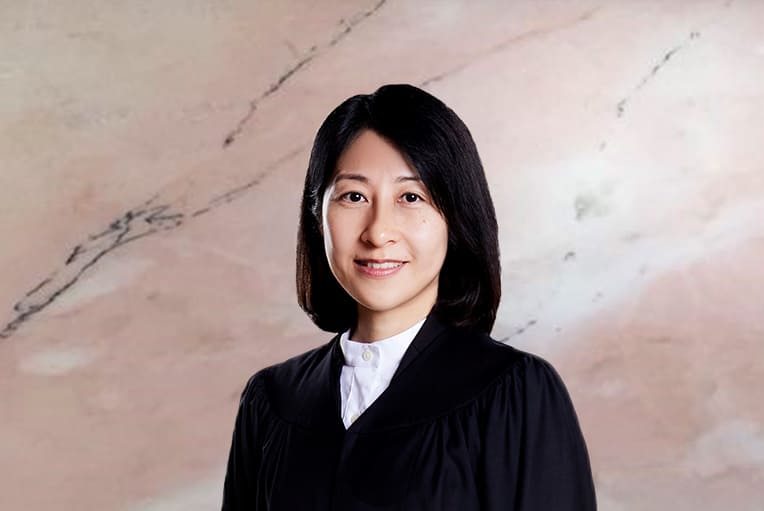
Deputy Registrar
Mr Teo Guan Siew
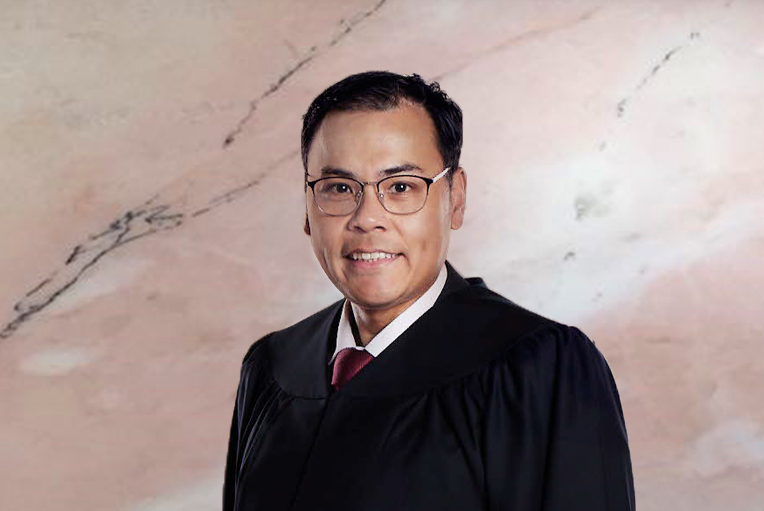
Senior Assistant Registrars
- Ms Ng Teng Teng, Cornie
- Ms Chong Chin Chin
- Ms Cheng Pei Feng
- Mr Lee Yeow Wee, David
Divisional Registrars
Court of Appeal and Appellate Division of the High Court | Ms Chong Chin Chin |
General Division of the High Court (Civil) |
|
| General Division of the High Court (Crime) |
|
Singapore International Commercial Court | Ms Crystal Tan Huiling |
Deputy Divisional Registrars
Court of Appeal and Appellate Division of the High Court |
|
| General Division of the High Court (Civil) |
|
| General Division of the High Court (Crime) |
|
Singapore International Commercial Court |
|
Assistant Registrars
|
|

































-1.png?sfvrsn=26b5fb9f_0)